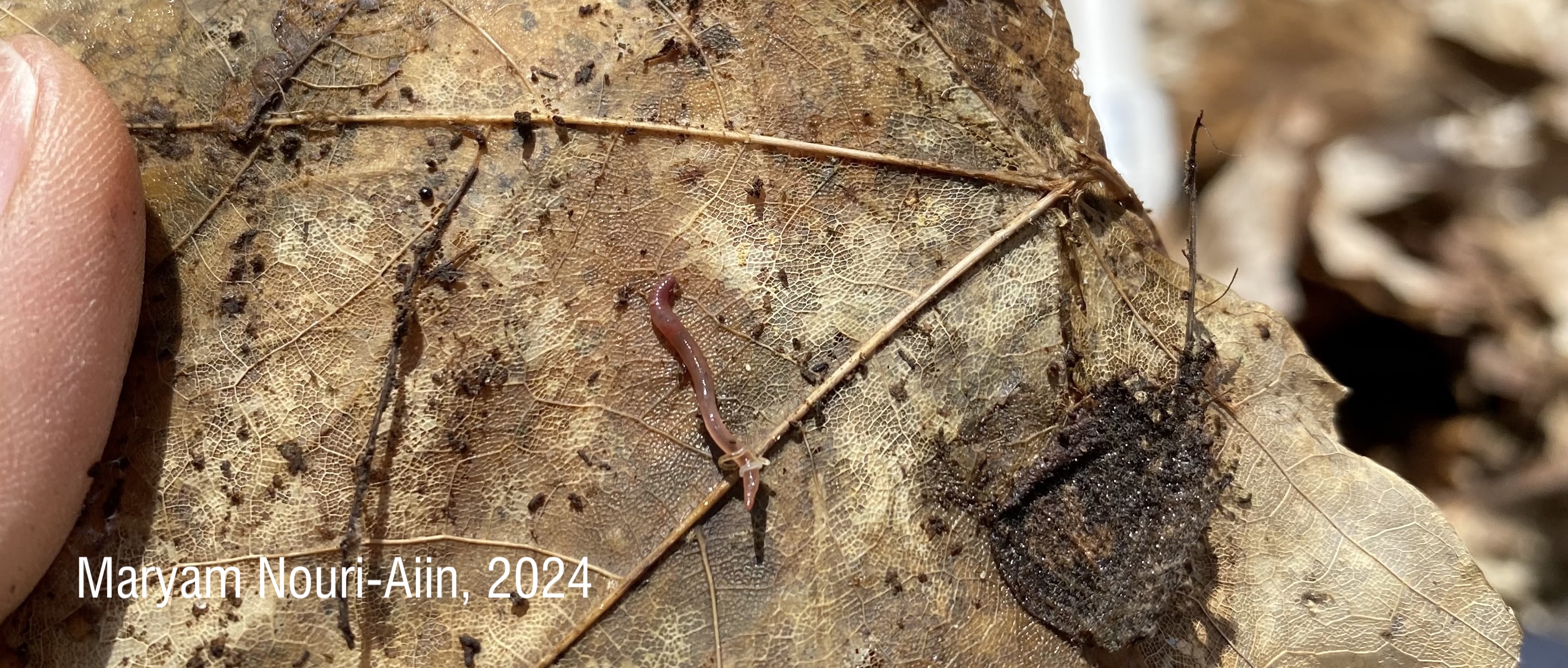
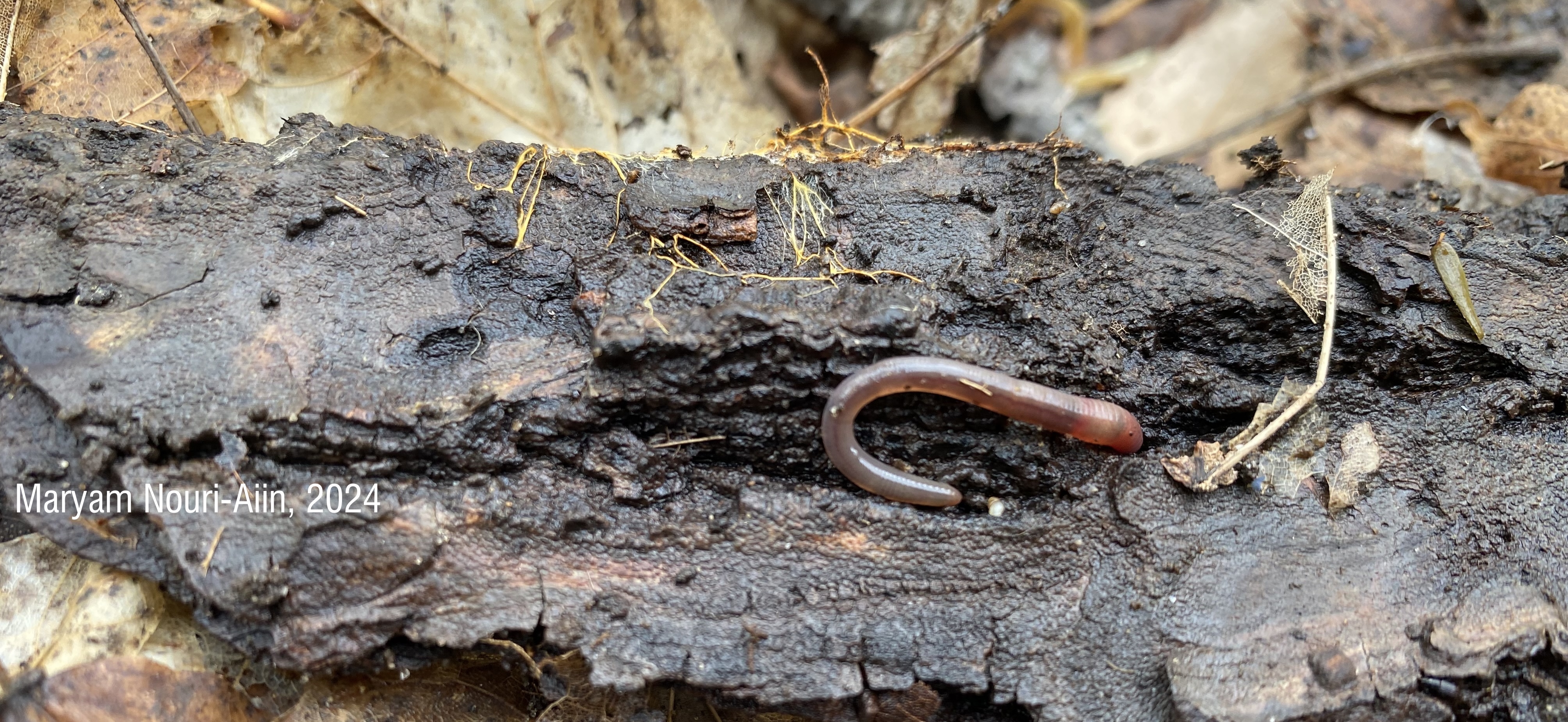
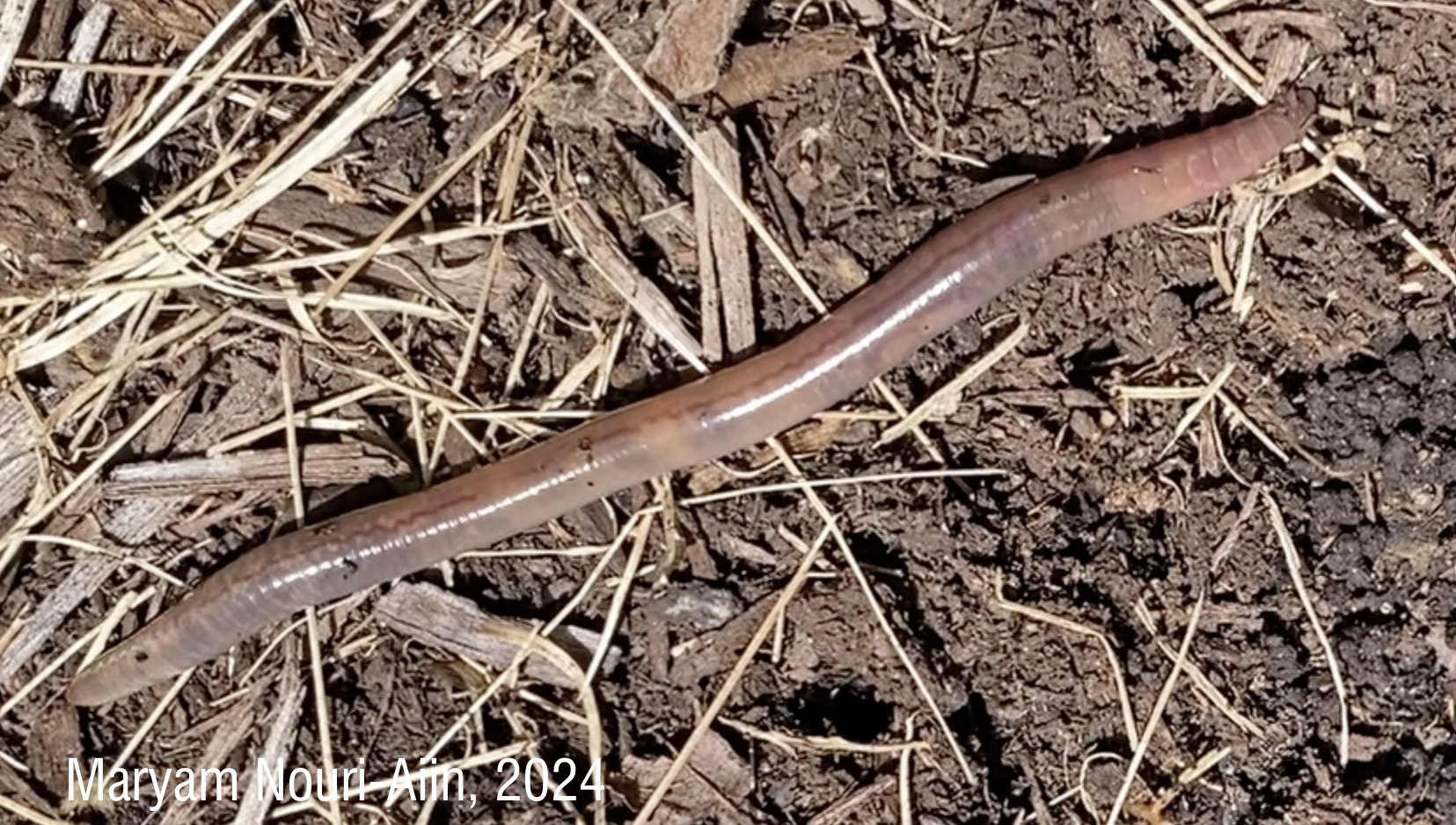
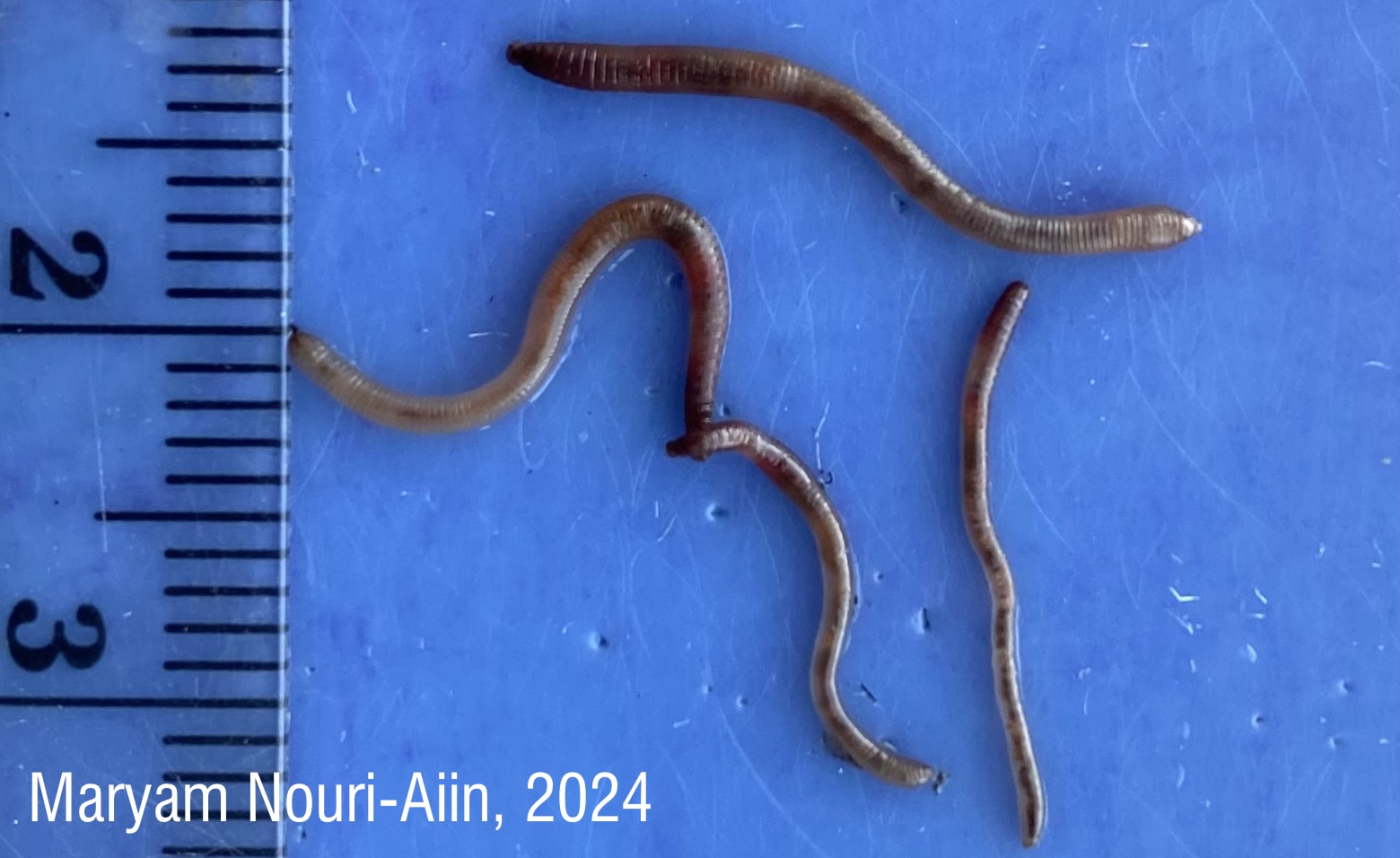
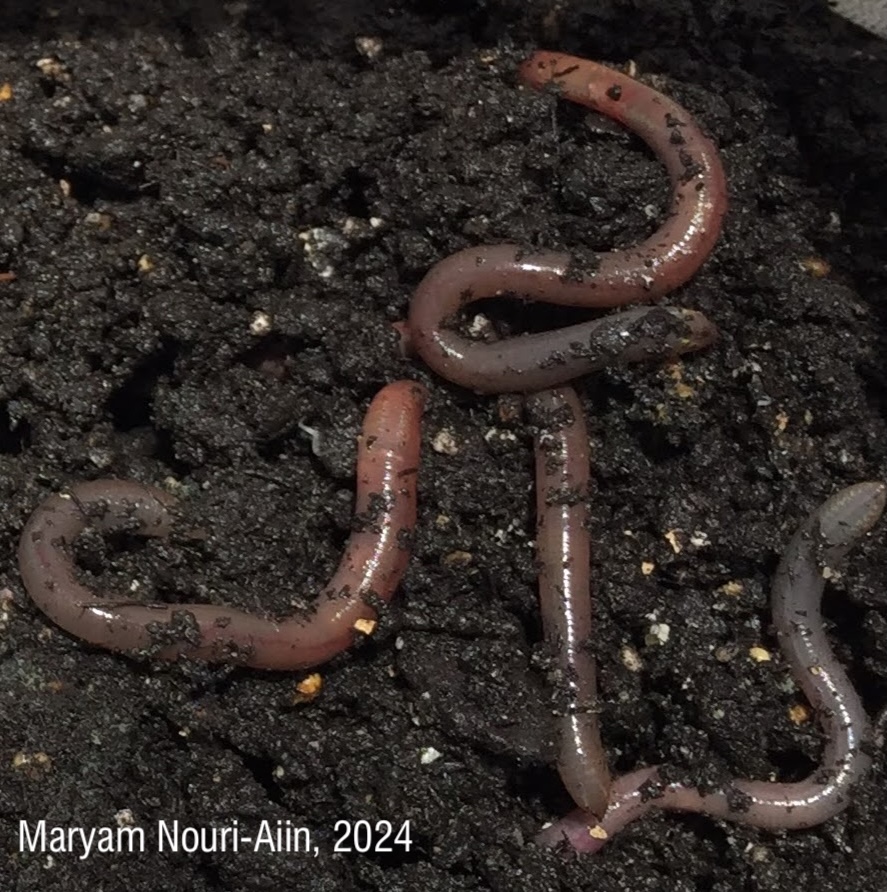
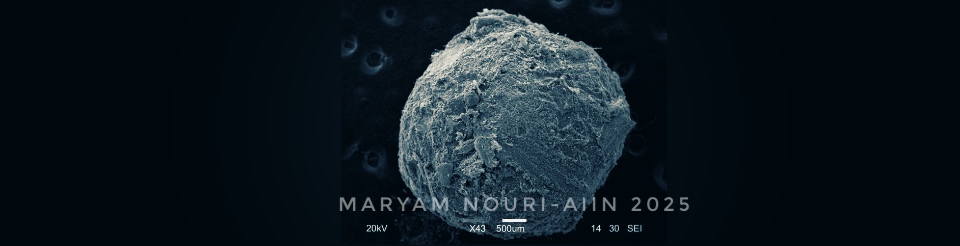
Identifying juvenile earthworms can be incredibly challenging due to their lack of distinguishing physical features. My paper presents a new method using multiplex PCR, which allows us to accurately identify cocoons, juvenile and adult jumping worms. This technique is faster, cheaper, and more reliable than previous approaches, making it a valuable tool for studying the spread and ecological effects of these earthworms.
Learn more about the method and its applications in Applied Soil Ecology .